Blended Learning Classroom Environments and Supporting Exceptional Learners
Blended Learning and its Models
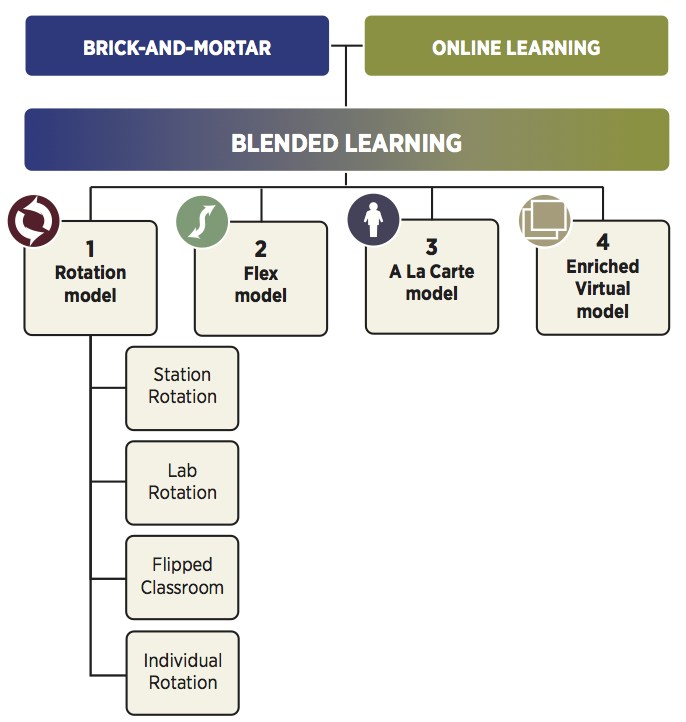
Blended learning refers to an approach to teaching which blends face-to-face instruction with online computer mediated learning (Ferdig, Cavanaugh, & Friedhoff, 2012). Post-secondary and high schools have been using blended learning models for some time to supplement class time with out-of-class interaction which can be student-to-student or student-to-content. In the elementary panel, blended learning models are now being adopted as teachers test various strategies to engage their learners in more meaningful ways. Blended learning models support teachers in being able to differentiate instruction, cater to individual student needs as well as foster critical thinking, and self motivation (McBain, 2011; Hodges & Webber, 2015). There are a number of variations of the model that fall under the blended learning umbrella. All of these variations are currently available to students, some through the public education system and some through private educational institutions.
(Horn & Staker, 2014)
Rotation Model - students work on a rotation schedule either working face-to-face with teachers or independently online. There are a number of variations to this model as well which can be implemented.
Flex Model - material is primarily delivered online however teachers are present in the room to provide support learning is self-directed.
A-la Carte Model - this model allows students to still attend a traditional school while taking supplementary courses completely online that are offered remotely.
Enriched Virtual Model - students work remotely and learning is self-directed, there is the option for face-to-face check-ins or students can choose to contact their instructors online. (Horn & Staker, 2012)
(Horn & Staker, 2014)
|
No comments:
Post a Comment